How does the mask law change from Saturday?
Where can we take off our mask from Saturday?
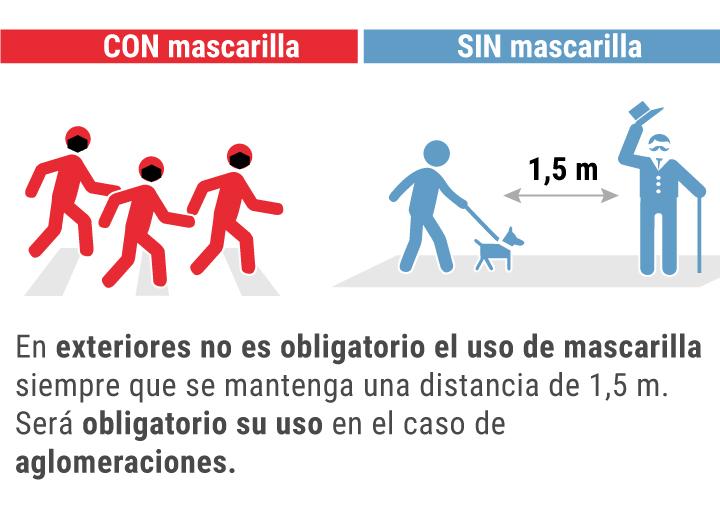
In outdoor spaces, as long as a distance of at least 1.5 meters is maintained from other people (unless they are cohabitants).
"We have only eliminated the obligation to wear a mask in those (situations) where we know there is less risk of transmission," said Carolina Darias, Minister of Health.
Where will its mandatory use be maintained?
In any type of public transport or if we meet people on the street with whom we have to interact.
In interior spaces, such as "a pharmacy or a supermarket", Darias has given as an example, it will continue to be mandatory to wear a mask.
What about concerts and outdoor events?
It will be mandatory in large events, even in open spaces, when the public is standing. For example, at an outdoor concert, unless the audience is seated and the distance of one and a half meters is maintained.
Will it be necessary to wear a mask in sports stadiums?
At the same time that the use of masks outdoors has been made more flexible, the article of the New Normality Law that limited the capacity at sporting events has been eliminated. The public is recovered in football stadiums and basketball courts.
Based on the general criteria, the use of a mask will be mandatory in closed venues, such as basketball courts, and also in open stadiums where distance is not maintained. As for the public limits, "the regional authorities will have to determine the capacity", explained Darias. "It will be a return to normality with joy, but complying with what we have just approved," she has expressed.
In what interiors is the mask removed?
It will no longer be mandatory in those residences for the elderly or other institutionalized spaces where 80% of the population of the residence is vaccinated.
But it will be mandatory for the people who work in that residence, because they are entering and leaving, and also for visitors.
How to fit cardio into your lifting routine: 1) do super low-intensity cardio on rest days 2) do it on a separate… https://t.co/ieY8QTMsIy
— Natalie Smith Sun Jan 03 00:03:02 +0000 2021
And in the interior spaces of essential professionals?
In units dedicated to special services, such as "a fire station", Darias has exemplified, it will not be mandatory to wear a mask as long as at least 80% are already vaccinated.
What will be its use in public transport?
Its use will be mandatory in any means of public transport: planes, trains, buses, taxis, boats... On boats or ships, its use will not be mandatory on deck if an interpersonal distance of 1.5 meters is maintained, and neither on private cabins.
Therefore, if a person goes out for a walk, but later decides to take public transport, he will not be able to get on if he has not worn a saved mask.
What technical criteria has inspired the Royal Decree?
"It will not be mandatory to wear a mask outdoors or in open spaces, as long as we respect the interpersonal distance of one and a half meters." That is, in the words of Darias, and with the exception of cohabiting persons, the fundamental criterion on which the new regulations are based. "Yes, it will be mandatory," therefore, "if there are crowds that prevent us from keeping our distance," the minister clarified.
In what specific situations do you have to continue wearing a mask and in which ones not?
The literalness of the Decree Law, according to the criteria set forth, leads to numerous situations in which the use of a mask continues to be mandatory, even outdoors, and especially in large cities. Whenever it is not possible to maintain a minimum distance of one and a half meters with a non-cohabiting person, it would be necessary to wear a mask. For example, when several pedestrians are waiting at a traffic light or when the sidewalk becomes crowded.
How does the new norm translate into day-to-day practice?
In practice, the new law is similar to the one approved in June 2020, which also established the need to wear a mask if you could not keep your distance and which, in practice, was never literally complied with: many people wore the mask on the street, but who decided not to do so, did not put it on suddenly when the sidewalk filled with people or passed very close to someone.
The same situation has been experienced with tobacco throughout the course: the mandatory use of a mask has been respected for the most part, but not the need to maintain a minimum distance when smoking. In fact, if a terrace where smoking is allowed is attached to the sidewalk and there is not enough width to pass, it is physically impossible to comply with the rule, a situation that occurs on numerous occasions and that, until now, had been compensated with the use mask universal.
What happens if an autonomous community does not want to adopt it?
It is a mandatory application standard throughout the national territory. Andalusia, which has the highest incidence in Spain in recent days, has been against the legislative change and will continue to recommend the use of an outdoor mask, although it will no longer be mandatory. Catalonia and Extremadura have already expressed their fear that it will be necessary to back down in the face of possible spikes in the summer.
What does the science say about masks in relation to SARS-CoV-2?
Scientific knowledge about the transmission routes of the virus has advanced throughout the pandemic. In the last spring, both the World Health Organization (WHO) and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Spanish Ministry of Health have modified their descriptions of the contagion mechanisms to give more weight to aerosols, whose risk is greater indoors.
However, the classic distinction between aerosols - which remain floating in the air as clouds of smoke - and droplets - which fall on surfaces - is also being revised. Although there is consensus that indoor spaces are more dangerous, both the WHO and the CDC highlight that the greatest risk of infection occurs at short distances, typically one meter or less. Therefore, it is possible to get infected outdoors, and hence the need to maintain interpersonal distance when we remove our mask outdoors.
Indoors, moreover, it is possible to become infected from more than a meter away, and even when the infectious person has already left the room, since the aerosol clouds can remain in the air and move from one side to another. Hence the importance of good ventilation and avoiding crowds in closed spaces, in addition to continuing to wear the mask in these places.
What have other countries done and what levels of vaccination did they have?
Comparing preventive measures and their real effect on populations in different countries is an arduous task, which often leads to confusion. For example, Israel and the US lifted the requirement to wear masks in many situations in April and May, respectively. Israel did so when more than 60% of the population had received at least one dose; USA, while approaching 50%, a situation similar to ours now.
In both cases, however, the decision was made when the vaccination campaign, which had progressed much faster during the winter, was beginning to stall. Both Israel and the US show a significant reduction in the rate of immunization from the dates on which, precisely, the use of masks was liberalized, so the measure can be understood as an incentive for the population with the greatest doubts to go and get vaccinated: the more people do it, the sooner the restrictions will go away. The same does not happen in Spain, where the percentage of vaccination is still advancing at a good pace.
In Europe, countries such as France or the city of Brussels, in Belgium, have withdrawn the obligation to wear masks in recent weeks. France did it after having more than 58% of the population with at least one dose - Spain has just exceeded 50% - and Belgium has administered almost 10 million doses to a total population of 11.5 million people. In fact, anyone who wants to receive Janssen's single-dose vaccine can now do so without an appointment at various points in the country. Both Belgium (73.1) and France (59.8) have incidences below that of Spain (92.57).
How many mask laws have there been and what are their differences?
The first regulation that made the use of masks mandatory was Royal Decree Law 21/2020, published on June 9, 2020, "on urgent prevention, containment and coordination measures to deal with the health crisis caused by COVID-19 ". That Decree already established the mandatory use of masks for people over six years of age, both in open and closed spaces, as long as the safety distance could not be maintained.
The exponential increase in outbreaks in summer and the widespread confusion about the distance criterion, impossible to meet in practice on a narrow sidewalk, for example, led the autonomous communities to tighten the rule on their own, each one your pace. At the beginning of autumn, with the second wave almost upon us, they had all done it.
Finally, the June 2020 rule was processed as a bill and gave rise to the Normality Law 2/21 of March 29, 2021, which was criticized for extending its use to any situation, even if you were alone in a open space. The new Royal Decree aims to put the situation in order and return to criteria similar to those of last summer, although it remains to be seen how the casuistry is defined by the Alerts Report and what is the actual compliance with the rule by the population.
According to the criteria of
The Trust ProjectLearn moreSATURATED NURSEOmicron symptoms: muscle pain, fatigue and headache, but without loss of taste or smellCovid-19China begins to vaccinate millions of children under 3 to 11 yearsCovidCases of coronavirus in Galicia increase for the ninth consecutive day